User Experience (UX)
Improved user experience and brand elevation for the staff and customers
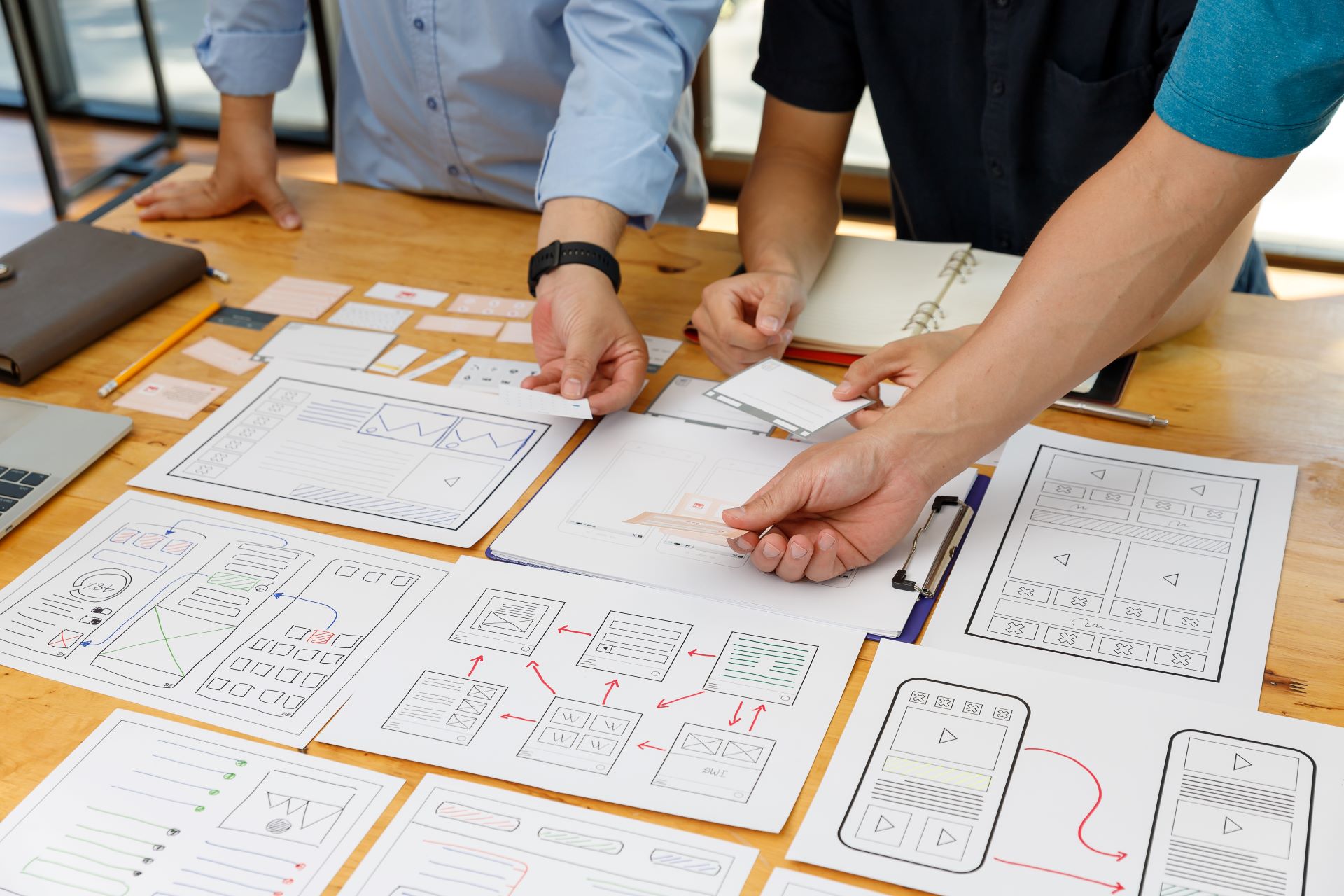

At Cherry White, we are passionate about creating exceptional user experiences that drive engagement and satisfaction.
Our UX services are meticulously designed to understand your users, craft intuitive interfaces, and ensure seamless interactions.
From user research to usability testing, we cover every aspect of UX to help your business stand out in the digital landscape.
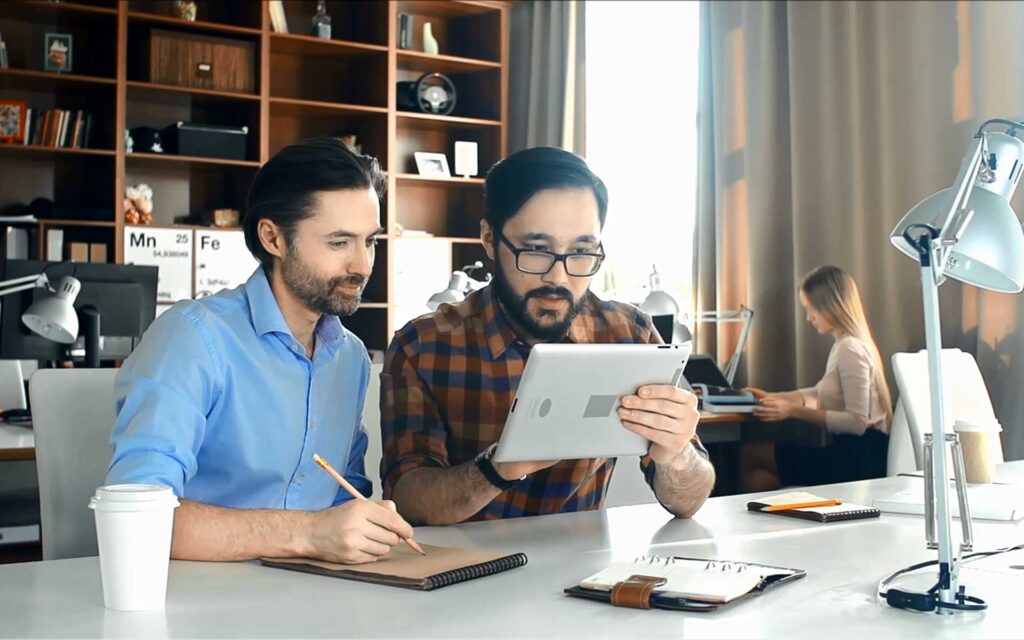

User Research and Analysis
Understanding your users is the foundation of effective UX design.
We conduct thorough user research to gain insights into your audience’s needs, behaviours, and pain points.
Our team employs various methods, including surveys, interviews, and usability studies, to gather valuable data. This analysis helps us create user personas and journey maps that guide the design process, ensuring that every decision is user-centric.
Information Architecture (IA)
A well-structured information architecture is crucial for a seamless user experience. We organise your content and features in a logical and intuitive manner, making it easy for users to find what they need.
Our IA services include creating sitemaps and wireframes that outline the structure of your website or application, ensuring a solid foundation for the design process.
Interaction Design
Interaction design focuses on creating engaging interfaces that are easy to use. We design interactive elements such as buttons, forms, and navigation menus with a keen eye on usability and aesthetics.
Our goal is to ensure that users can interact with your digital product effortlessly, leading to a more satisfying experience.
Visual design
Visual design is where functionality meets aesthetics. Our designers craft visually appealing interfaces that reflect your brand’s identity and resonate with your audience.
We pay close attention to colour schemes, typography, imagery, and overall layout to create a cohesive and attractive design. The result is a digital product that is not only functional but also delightful to use.
Prototyping
Prototyping is a critical step in the UX design process, allowing us to create interactive models of your digital product. These prototypes enable us to test and refine the user experience before development begins.
By simulating real-world interactions, we can identify and address potential issues early, saving time and resources in the long run.
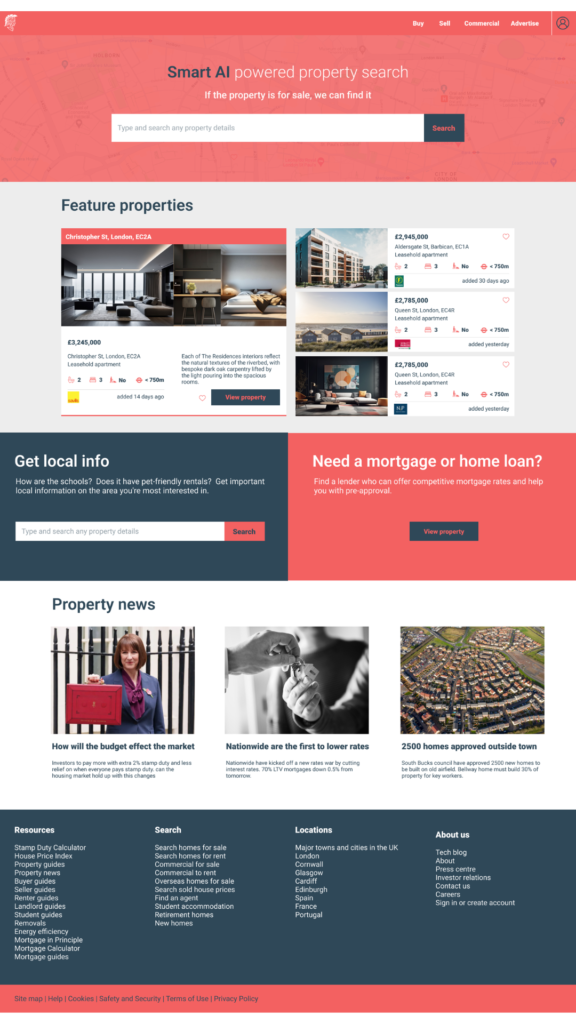
Usability testing
Usability testing ensures that our designs meet the needs and expectations of your users. We conduct testing sessions with real users to gather feedback and observe how they interact with your digital product.
This process helps us identify usability issues and make necessary adjustments to enhance the overall user experience.
Continuous improvements
UX design is an ongoing process. We believe in continuously improving and iterating on our designs based on user feedback and analytics.
By regularly assessing and refining the user experience, we ensure that your digital product remains relevant and effective in meeting your users’ needs.

Why Choose Cherry White for UX Services?
At Cherry White, we combine creativity with a deep understanding of user behaviour to create exceptional digital experiences.
Our team of experts is dedicated to delivering user-centric designs that not only look great but also function flawlessly.
We take a holistic approach to UX, covering every aspect from research and analysis to design and testing, ensuring that your digital product stands out in a competitive market.
Transform your user experience with Cherry White. Contact us today to learn more about our UX services and how we can help you create digital products that delight and engage your users.

